Getting Started with the VMware vCenter Integration for NetBox
This guide will help you set up and start using the VMware vCenter Integration for NetBox.
- Prerequisites
- Site Organization with vCenter Tags
- Host Requirements
- NetBox Setup
- Agent Setup and Configuration
- Step 2: Configure the Agent
- Expected Output
- View and Apply Discovered Data in NetBox Assurance
- View the VMware vCenter Data in NetBox
- Additional Resources
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following:
- NetBox Cloud or NetBox Enterprise with NetBox Assurance
- Orb Agent Pro credentials (required to download the integration agent image)
- vCenter Servers(s) with API access
- Host System with Docker support
- Network connectivity between your host(s) and both NetBox instance and the vCenter Servers(s)
Site Organization with vCenter Tags
The VMware vCenter integration supports automatic site creation in NetBox based on tags applied to ESXi hosts in vCenter. This allows you to organize your virtual infrastructure by physical locations, data centers, or any other logical grouping.
How Site Tagging Works
The integration scans all ESXi hosts in your vCenter environment and looks for tags with the format:
netbox_site:<site_name>
Examples:
netbox_site:NYC-Datacenternetbox_site:London-Officenetbox_site:Production-Floor-1
Setting Up Site Tags in vCenter
-
Create a Tag Category (if not already exists):
- In vCenter, go to Tags & Custom Attributes → Categories
- Create a new category named
netbox-sites - Set the cardinality to "Many" to allow multiple tags per object
- Set the associable object types to include "Host System"
-
Create Site Tags:
- Go to Tags & Custom Attributes → Tags
- Create tags with the naming convention:
netbox_site:<your-site-name> - Assign the tag to the
netbox-sitescategory
-
Apply Tags to Hosts:
- Right-click on each ESXi host
- Select Tags & Custom Attributes → Assign Tag
- Choose the appropriate
netbox_site:<site-name>tag
Site Creation Behavior
- With Tags: If hosts have
netbox_site:tags, the integration creates NetBox sites for each unique site name - Without Tags: If no hosts have site tags, the integration creates a single
DefaultSitein NetBox - Mixed Environment: Hosts with tags are assigned to their respective sites, hosts without tags are assigned to
DefaultSite
Best Practices
- Use descriptive, consistent naming for your site tags
- Apply site tags to all ESXi hosts for better organization
- Consider your physical infrastructure layout when naming sites
- Test with a few hosts first before applying tags organization-wide
Host Requirements
System
- Operating System: Linux, macOS, or Windows with Docker support
- Memory: Minimum 2GB RAM (4GB recommended)
- Storage: 1GB free disk space
- Network: Stable internet connection for pulling Docker images
- Docker: Version 20.10 or later
Network
- Outbound gRPC/gRPCS access to Diode on your NetBox instance (typically port 443 for gRPCS)
- Outbound HTTP/HTTPS access to your vCenter server (typically port 443 for HTTPS)
- DNS resolution for both NetBox and vCenter server hostnames
- Firewall rules configured to allow the above connections from your agent host
NetBox Setup
Generate Diode Client Credentials
- Log into your NetBox instance
- Navigate to Diode → Client Credentials
- Click + Add a Credential
- Enter a descriptive name (e.g., "vCenter Integration")
- Click Create
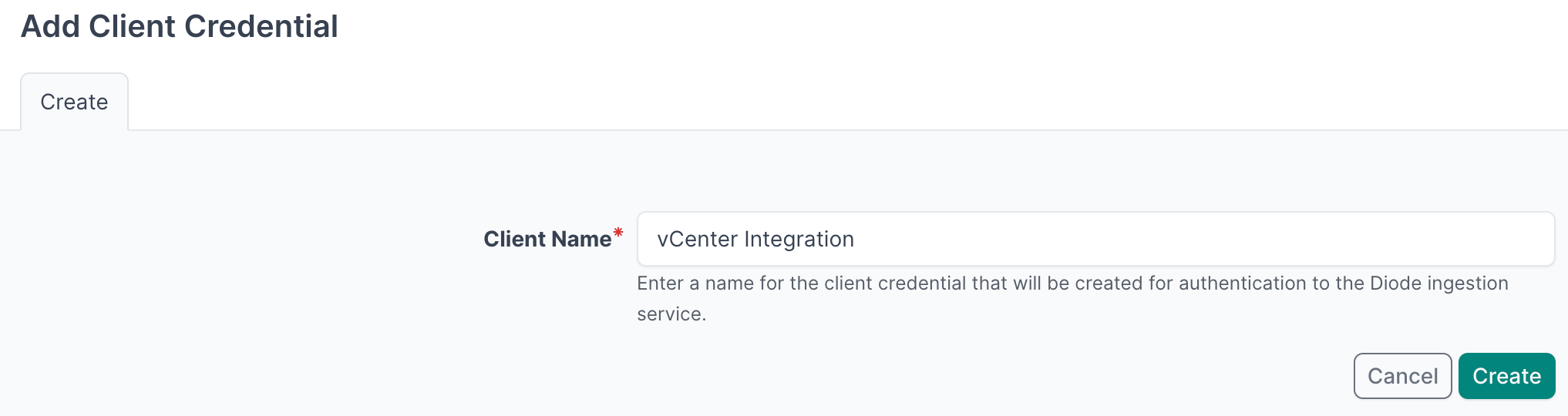
- Important: Copy and securely store the Client ID and Client Secret as you will reference this in the agent configuration file in later steps
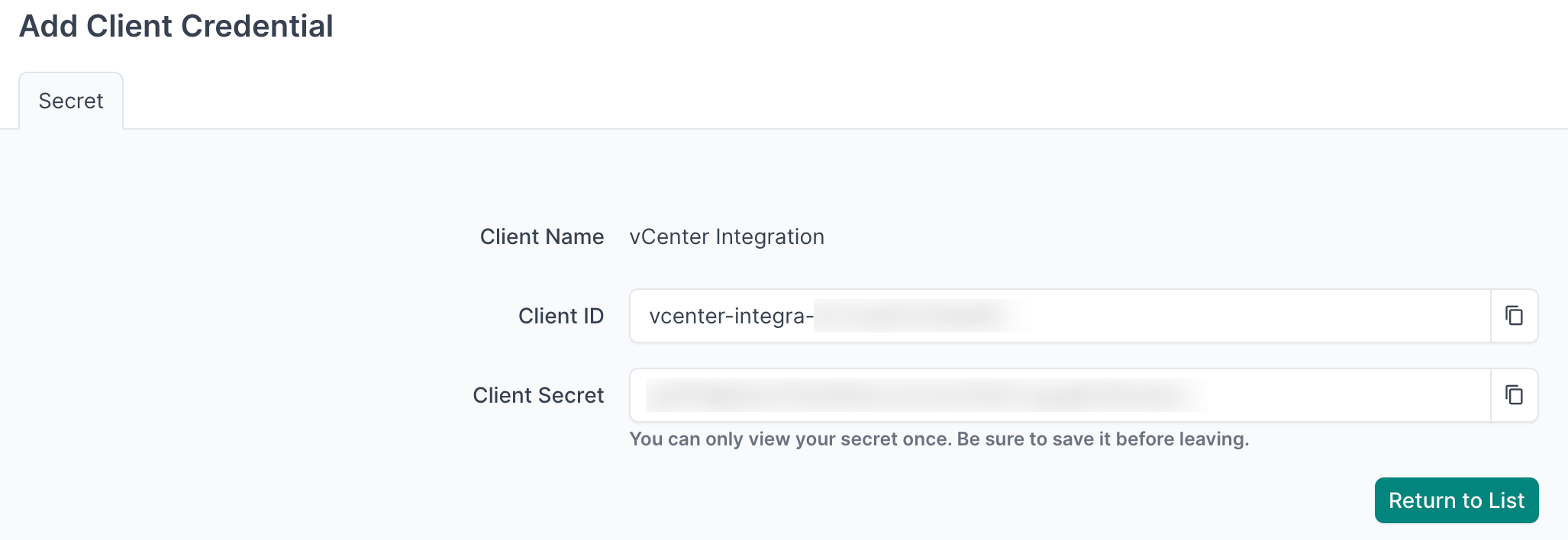
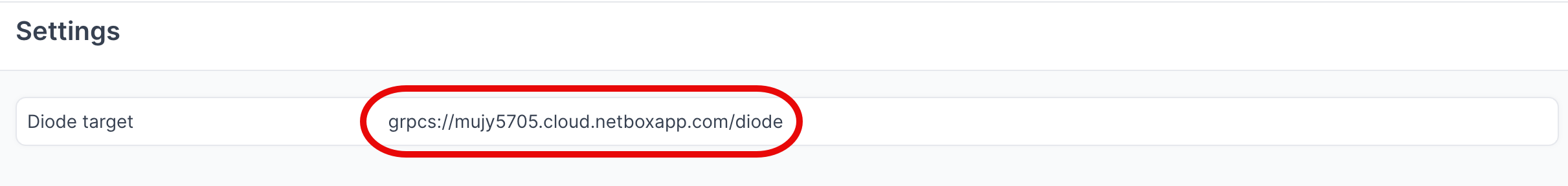
- Navigate to Diode → Settings
- Copy the value of the Diode target as you will reference this in the agent configuration file in later steps
Agent Setup and Configuration
You can deploy multiple agents configured to sync data from more than one vCenter Server
Step 1: Authenticate to the NetBox Labs Image Registry
From your host machine, authenticate to the NetBox Labs registry, using the CUSTOMER-IDENTIFIER and Token that you have been provided by the NetBox Labs team:
docker login -u<CUSTOMER-IDENTIFIER> netboxlabs.jfrog.io
Example session
% docker login -u<customer-abc123> netboxlabs.jfrog.io # note there are no spaces after -u
# Use the Token provided as the password when prompted
Password:
Login Succeeded
Step 2: Configure the Agent
- Create the configuration file (you can name the file anything you like):
touch agent.yaml
- Edit the configuration file with your preferred editor and add the following configuration. Important: Replace
grpcs://your-instance.netboxcloud.com/diodewith the value from Diode > Settings > Diode target in the NetBox UI:
orb:
config_manager:
active: local
backends:
worker:
common:
diode:
target: grpcs://your-instance.netboxcloud.com/diode # Get this value from Diode > Settings > Diode target
client_id: ${DIODE_CLIENT_ID}
client_secret: ${DIODE_CLIENT_SECRET}
agent_name: vmware_vcenter_01 # Use a meaningful name to identify this agent
policies:
worker:
vmware_vcenter_center_worker:
config:
package: nbl_vmware_vcenter
schedule: "0 2 * * *" # Daily at 2:00 AM. Set your desired schedule (see examples below)
timeout: 5
VCENTER_HOST: ${VCENTER_HOST}
VCENTER_USER: ${VCENTER_USER}
VCENTER_PWD: ${VCENTER_PWD}
SKIP_SSL: True # Optional setting to skip SSL verification
BOOTSTRAP: True # Set to True for initial setup, False for regular operation
scope:
datacenters: ["NYC1"] # Optional: Limit sync to specific datacenters (see scope configuration below)
The schedule field uses cron syntax. Here are some common examples:
"0 */6 * * *"- Every 6 hours (e.g., 00:00, 06:00, 12:00, 18:00)"0 2 * * *"- Daily at 2:00 AM"0 9 * * 1"- Weekly on Monday at 9:00 AM
Scope Configuration
The scope section allows you to limit the data synchronization to specific datacenters, reducing the amount of data processed and improving performance.
Configuration Options:
["*"]or omitted: Syncs all datacenters (default)["Datacenter-A", "Datacenter-B"]: Syncs only specified datacenters and their VMs- VMs from filtered datacenters are excluded from synchronization
- VMs without datacenter assignment are always included
- Invalid datacenter names raise an error with available datacenter list
Example:
scope:
datacenters: ["NYC1", "LAX1"] # Only sync these specific datacenters
Site Organization with Tags
The integration automatically creates NetBox sites based on netbox_site: tags applied to ESXi hosts in vCenter. This provides better organization of your virtual infrastructure.
Tag Format:
- Use the format:
netbox_site:<site_name> - Examples:
netbox_site:NYC-Datacenter,netbox_site:London-Office
Setup in vCenter:
- Create a tag category named
netbox-sitesfor "Host System" objects - Create tags with the
netbox_site:<site-name>naming convention - Apply the appropriate tag to each ESXi host
Behavior:
- Hosts with
netbox_site:tags → Assigned to corresponding NetBox sites - Hosts without tags → Assigned to
DefaultSite - Each unique site name creates a separate NetBox site
Bootstrap Mode (First-Time Setup)
Bootstrap mode is used for the initial setup only of the integration. When enabled, it creates static content in NetBox that the integration requires to function properly.
What Bootstrap Mode Does:
- Creates required Manufacturers
- Creates necessary Tags
- Creates required Custom Fields
- Sets up initial data structures
Configuration:
config:
BOOTSTRAP: True # Set to True for initial setup, False for regular operation
First-Time Run Process:
- Run the agent with
BOOTSTRAP: Truein your configuration - Monitor the output for the text
executed successfully - Stop the agent immediately by pressing
Ctrl+Cin your terminal once you seeexecuted successfully - Apply the deviations in NetBox Assurance (see Apply Deviations section below)
- Set
BOOTSTRAP: Falsefor all future runs
Important Notes:
- Bootstrap mode is only for first-time setup - do not run it on a schedule
- You must stop the agent manually with
Ctrl+Cafter seeingexecuted successfully - After bootstrap, you'll see deviations for Custom Fields, Manufacturers, etc. that must be applied
- Once deviations are applied, set
BOOTSTRAP: Falsefor regular operation
Optional - Dry Run Mode
The agent can be run in Dry Run mode, which means discovered data is written to a json formatted file instead of to NetBox. This can be useful for troubleshooting - for example you could share the file with the NetBox Labs support team to investigate issues ingesting certain data.
Enable this in the Diode section of your agent configuration file, by adding the dry_run key and setting the value to true (it is false by default) and set the dry_run_output_dir value to the location you want the file to be saved.
diode:
dry_run: true
dry_run_output_dir: /opt/orb/ # this will save the output file into the same directory that you run the agent from
Step 3: Run the Agent
Run the agent to synchronize data from your vCenter server into NetBox:
Method 1: Set Environment Variables Manually
- Export Diode credentials as environment variables:
export DIODE_CLIENT_ID="your-client-id"
export DIODE_CLIENT_SECRET="your-client-secret"
- Export vCenter credentials as environment variables:
export VCENTER_HOST="your-vcenter-server"
export VCENTER_USER="your-vcenter-username"
export VCENTER_PWD="your-vcenter-password"
- Run the agent with the following command:
docker run \
-v $PWD:/opt/orb/ \
-e DIODE_CLIENT_SECRET \
-e DIODE_CLIENT_ID \
-e VCENTER_HOST \
-e VCENTER_USER \
-e vCENTER_PWD \
netboxlabs.jfrog.io/obs-orb-agent-pro/orb-agent-pro \
run -c /opt/orb/agent.yaml
Method 2: Use a .env File (Recommended)
- Create a
.envfile in your current directory:
touch .env
- Edit the
.envfile with your preferred editor and add the following content:
## NetBox Diode credentials (from Step 1)
DIODE_CLIENT_ID=your-client-id
DIODE_CLIENT_SECRET=your-client-secret
## VMware vCenter credentials
VCENTER_HOST=your-vcenter-server
VCENTER_USER=your-vcenter-username
VCENTER_PWD=your-vcenter-password
Replace the placeholder values with your actual credentials:
your-client-idandyour-client-secretfrom the NetBox Diode setupyour-vcenter-serverwith your vCenter server hostname or IP addressyour-vcenter-usernameandyour-vcenter-passwordwith your vCenter credentials
- Run the agent with the following command:
docker run \
-v $PWD:/opt/orb/ \
--env-file .env \
netboxlabs.jfrog.io/obs-orb-agent-pro/orb-agent-pro \
run -c /opt/orb/agent.yaml
When using Method 2, add .env to your .gitignore file to prevent accidentally committing sensitive credentials to version control:
echo ".env" >> .gitignore
Expected Output
After you issue the command to run the agent, depending on the schedule you defined in the configuration file, you should see similar to the output below:
...
{"time":"2025-08-21T10:25:58.237832544Z","level":"INFO","msg":"worker stderr","log":"INFO:nbl_vmware_vcenter.vcenter_diode:Processing vCenter 192.168.0.101"}
{"time":"2025-08-21T10:25:58.237858003Z","level":"INFO","msg":"worker stderr","log":"INFO:nbl_vmware_vcenter.vcenter_diode:Connecting to vCenter..."}
{"time":"2025-08-21T10:25:58.238308128Z","level":"INFO","msg":"worker stderr","log":"INFO:apscheduler.scheduler:Removed job 2ee353d8ba36461c88c82d32585f85f0"}
{"time":"2025-08-21T10:25:58.351597961Z","level":"INFO","msg":"worker stderr","log":"INFO:nbl_vmware_vcenter.vcenter_diode:Connected to vCenter."}
{"time":"2025-08-21T10:25:58.351624253Z","level":"INFO","msg":"worker stderr","log":"INFO:nbl_vmware_vcenter.vcenter_diode:Building entities for Diode ingestion..."}
{"time":"2025-08-21T10:25:58.94254067Z","level":"INFO","msg":"worker stderr","log":"INFO:nbl_vmware_vcenter.vcenter_diode:Created Site entity: NYC-Datacenter"}
{"time":"2025-08-21T10:25:58.94254068Z","level":"INFO","msg":"worker stderr","log":"INFO:nbl_vmware_vcenter.vcenter_diode:Created Site entity: London-Office"}
{"time":"2025-08-21T10:26:00.674980754Z","level":"INFO","msg":"worker stderr","log":"INFO:nbl_vmware_vcenter.vcenter_diode:Added host entity: esx-01.nyc.local (site: NYC-Datacenter)"}
{"time":"2025-08-21T10:26:00.674980755Z","level":"INFO","msg":"worker stderr","log":"INFO:nbl_vmware_vcenter.vcenter_diode:Added host entity: esx-02.london.local (site: London-Office)"}
{"time":"2025-08-21T10:26:00.704773171Z","level":"INFO","msg":"worker stderr","log":"INFO:worker.policy.runner:Policy vmware_vcenter_worker: Successful ingestion"}
{"time":"2025-08-21T10:26:00.704934462Z","level":"INFO","msg":"worker stderr","log":"INFO:apscheduler.executors.default:Job \"PolicyRunner.run (trigger: date[2025-08-21 10:25:58 UTC], next run at: 2025-08-21 10:25:58 UTC)\" executed successfully"}
If you have configured netbox_site: tags on your ESXi hosts, you'll see log entries like:
Created Site entity: <site-name>- for each unique site discovered from tagsAdded host entity: <hostname> (site: <site-name>)- showing which site each host is assigned to
If no site tags are found, you'll see:
No site tags found, creating default site- and all hosts will be assigned toDefaultSite
Success Indicators: Look for the text Successful ingestion in the output, which confirms that data was successfully sent to your NetBox instance via Diode.
Testing Mode: For testing purposes, you can run the agent once and then stop it:
- Press
Ctrl+Cin your terminal to stop the agent - This is useful for verifying configuration before setting up continuous operation
Continuous Operation: The agent will continue running according to your schedule until manually stopped or the container is terminated.
View and Apply Discovered Data in NetBox Assurance
You can now work with the vCenter data that has been discovered by the agent in the NetBox Assurance UI.
NetBox Assurance gives you control over operational drift by identifying deviations between your operational state and NetBox, and analytics to understand drift and plan for remediation, and ultimately take action.
Deviations are the delta between the data already in NetBox as the Network Source of Truth, versus the actual operational state of the network as discovered by the controller integration.
From an initial run of the integration it could be that ALL discovered data is a deviation as it may not have existed in NetBox previously. Once the initial sync of data has taken place, and NetBox has been updated, then further integration runs would result in new deviations only.
Accessing NetBox Assurance
- Navigate to the UI of NetBox instance
- Click on Assurance in the main navigation menu
Explore Deviation Types
- Click on Deviation Types to view the types of deviations that have been discovered
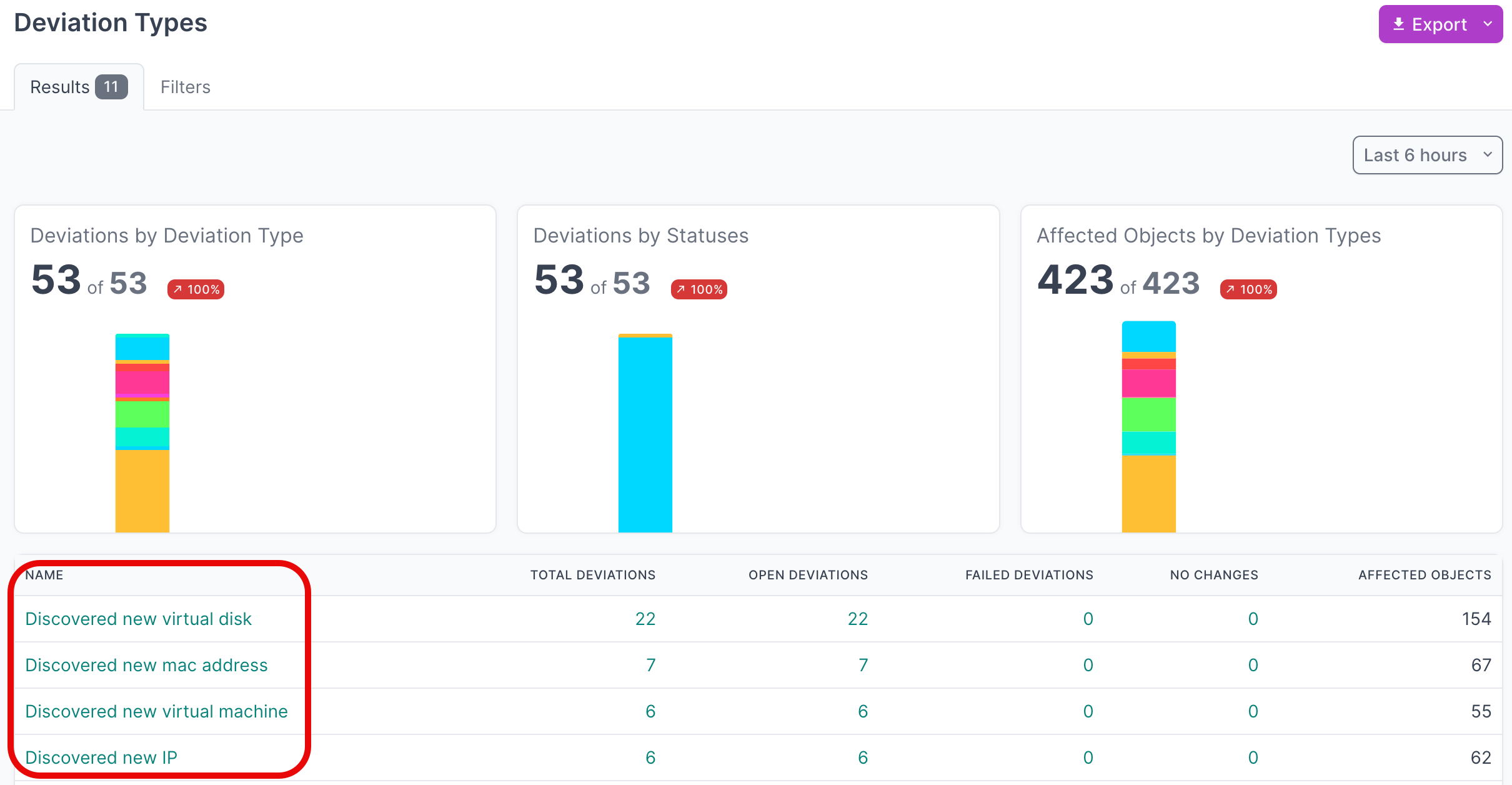
- Click on the Name of a deviation type, to view deviations for a particular type
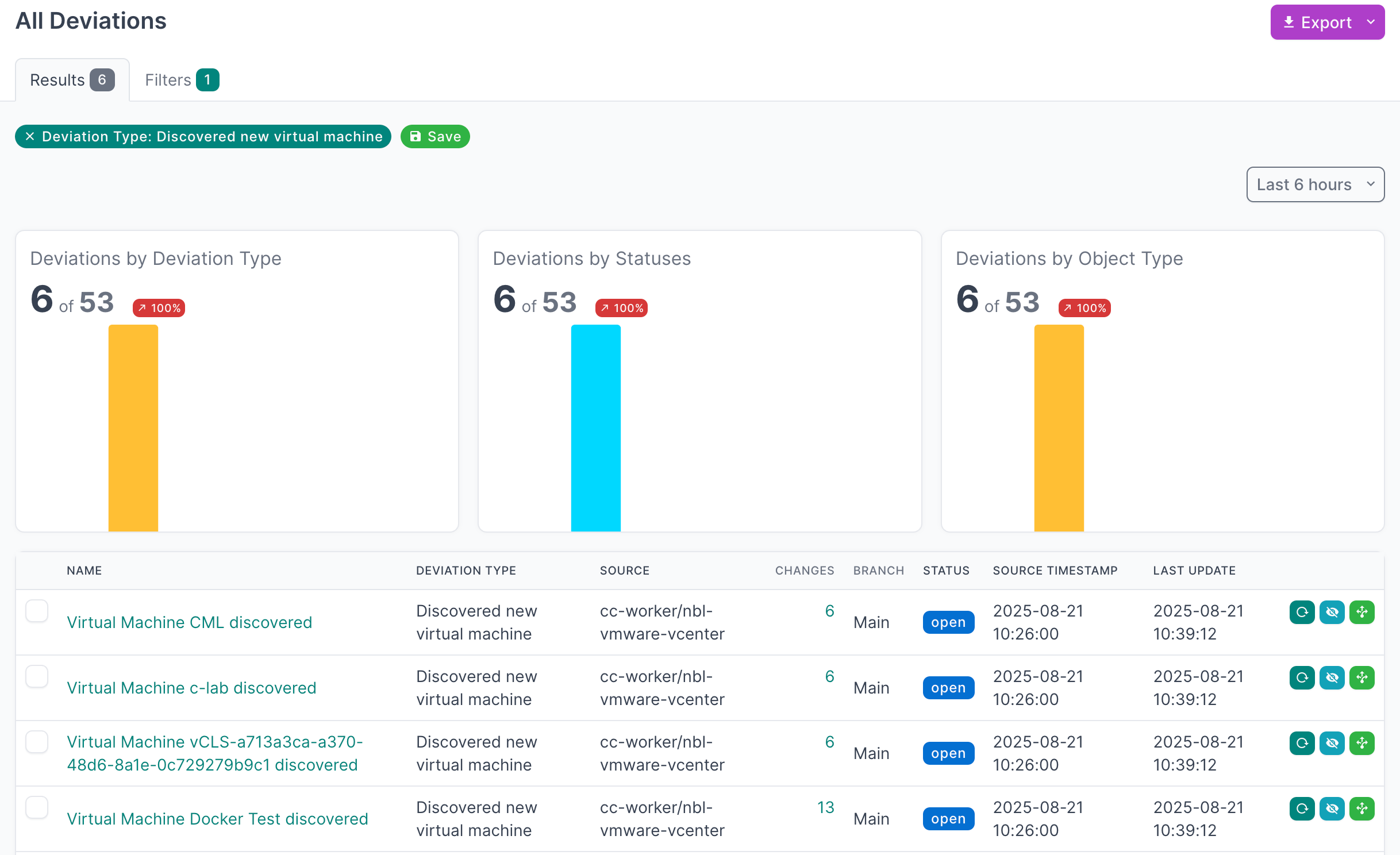
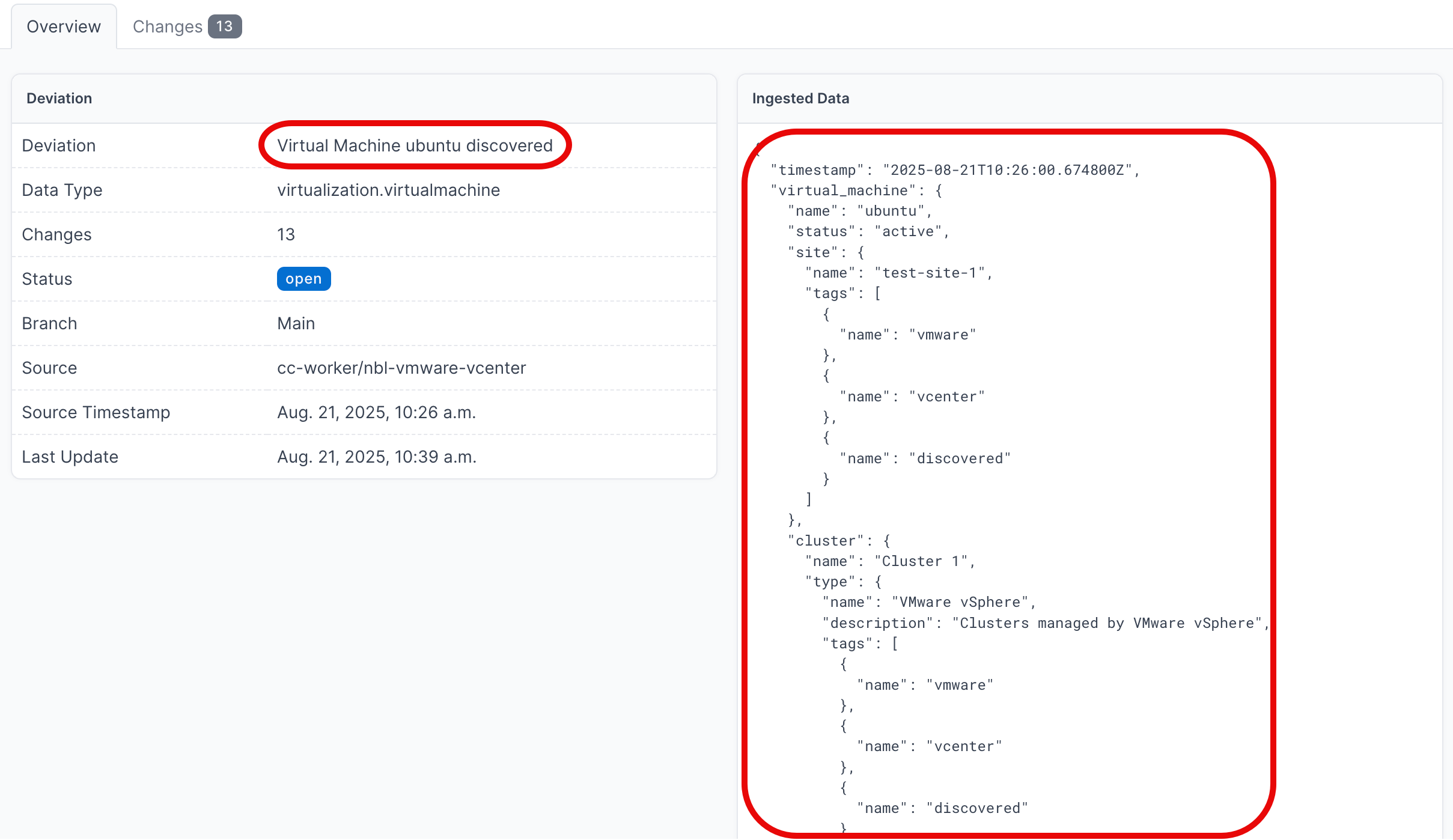
- Click on the Name of a an individual deviation, to view the details
View Active Deviations
- Click on Active Deviations to view all the deviations that have not yet been Applied or Ignored
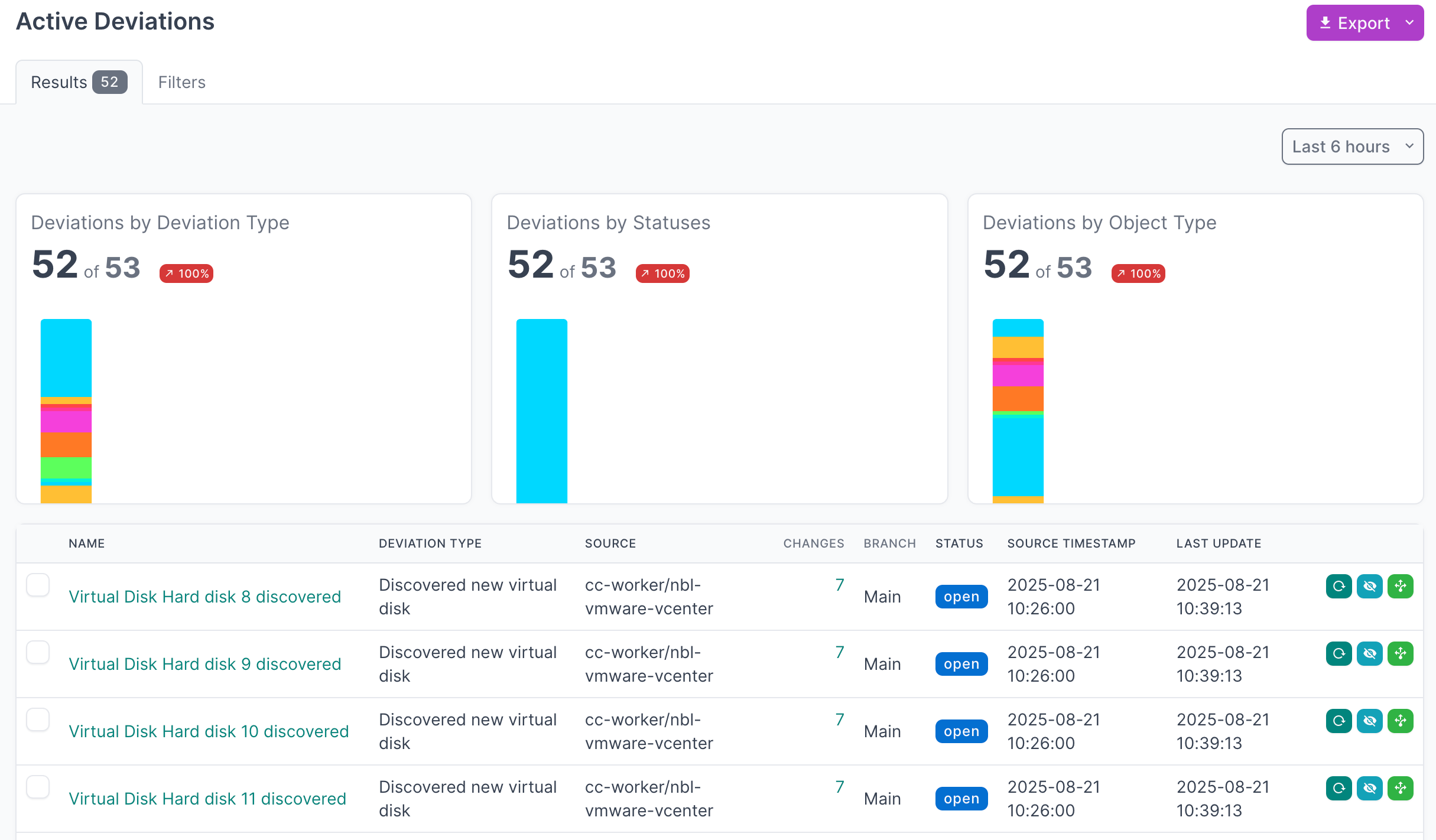
- Click on the Name of a deviation, to view the details
Apply Deviations
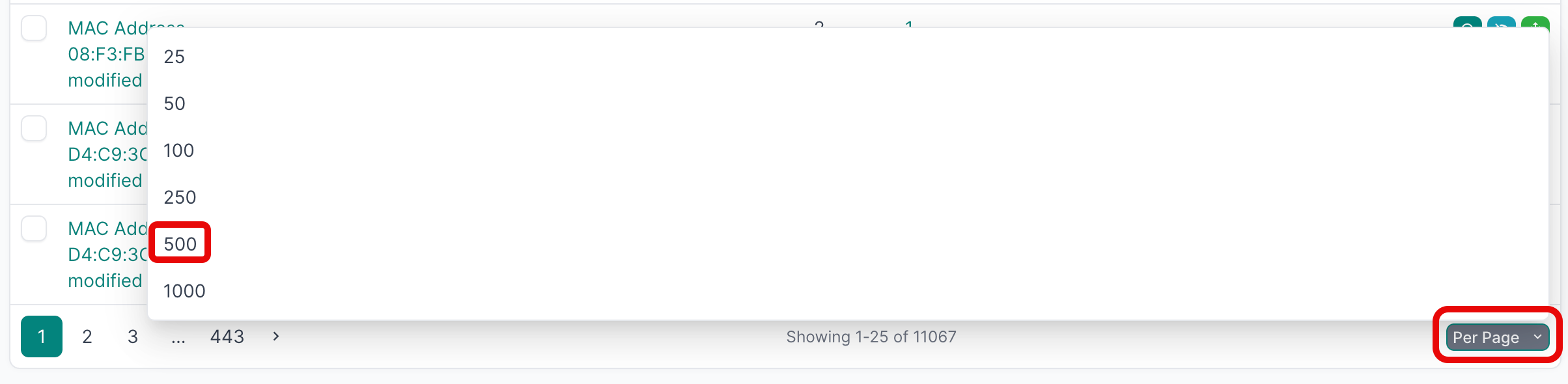
- Select all the deviations that you'd like to apply. If you are working with a large number of deviations, first set the Per Page view to 500:
- Then select the first deviation, hold down
SHIFTand select the last one, and then click Apply Selected: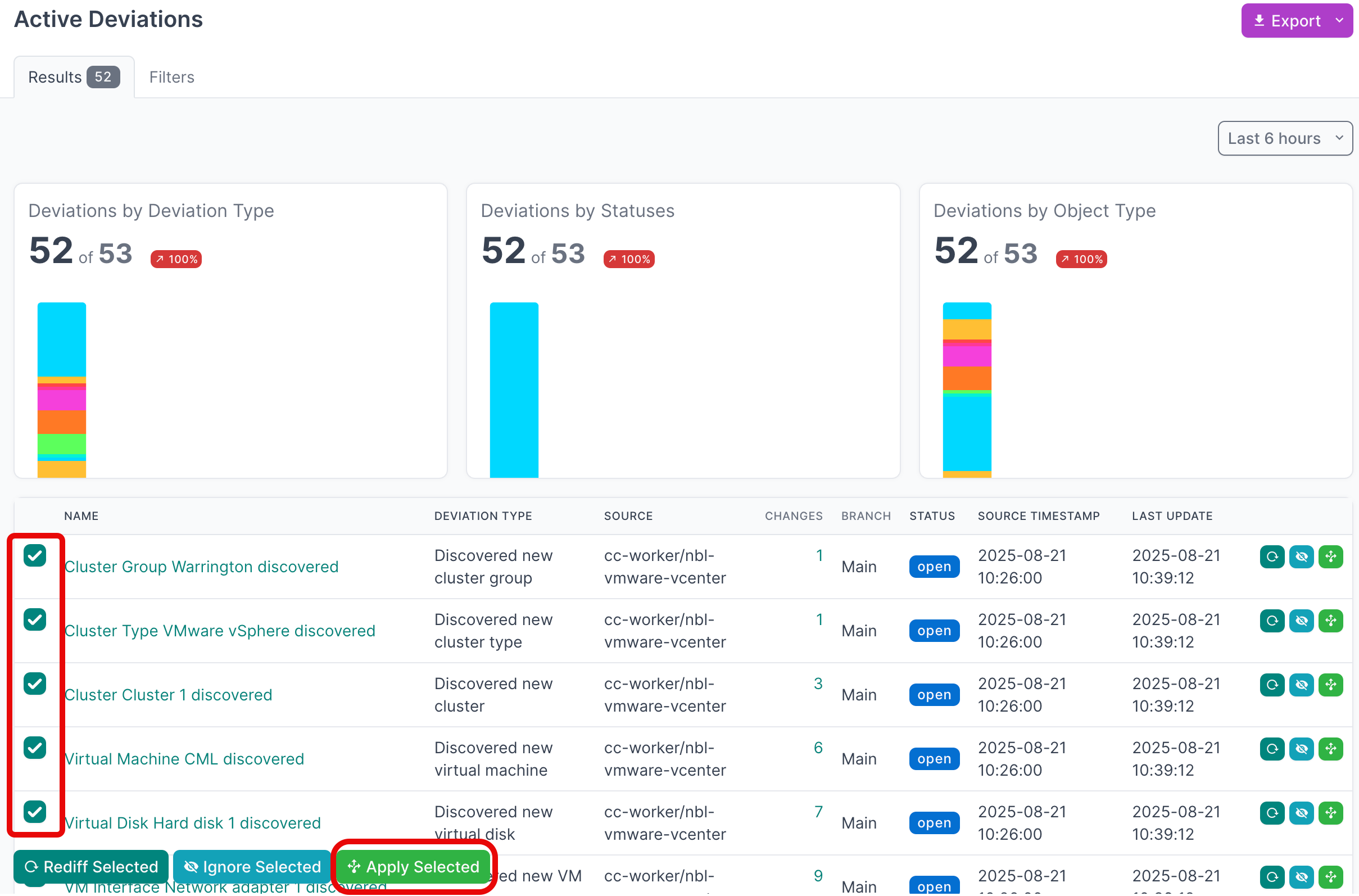
- Click Apply X Deviations to apply the deviations to the NetBox database:
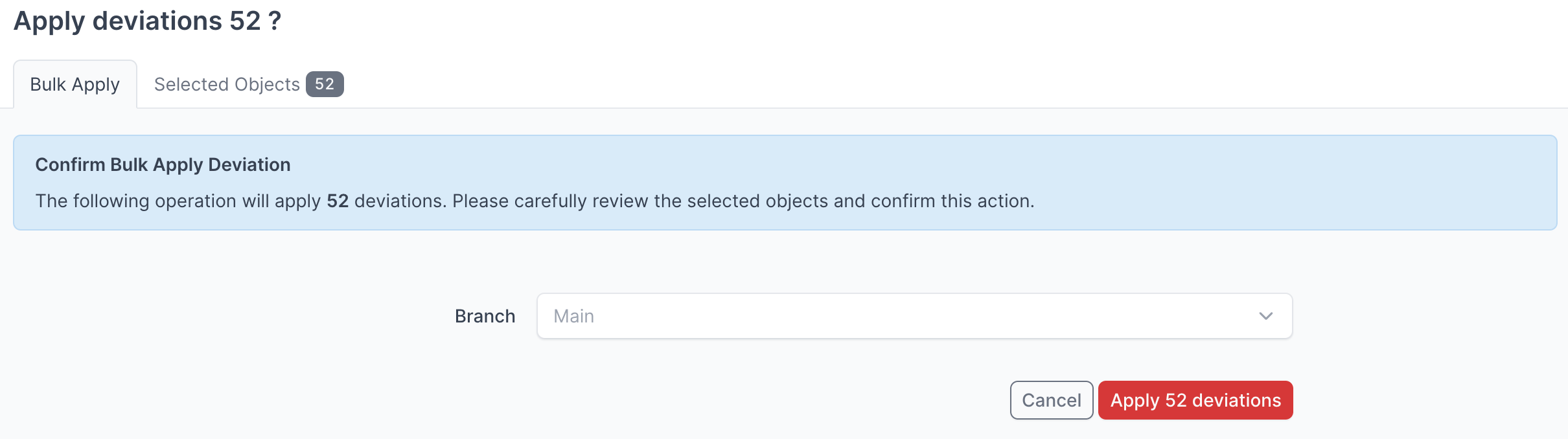
Instead of writing the deviations to the Main NetBox database branch, you can select another branch from the drop down menu and apply the deviations to that branch.
For more detailed information on working with NetBox Assurance, please refer to the documentation
View the VMware vCenter Data in NetBox
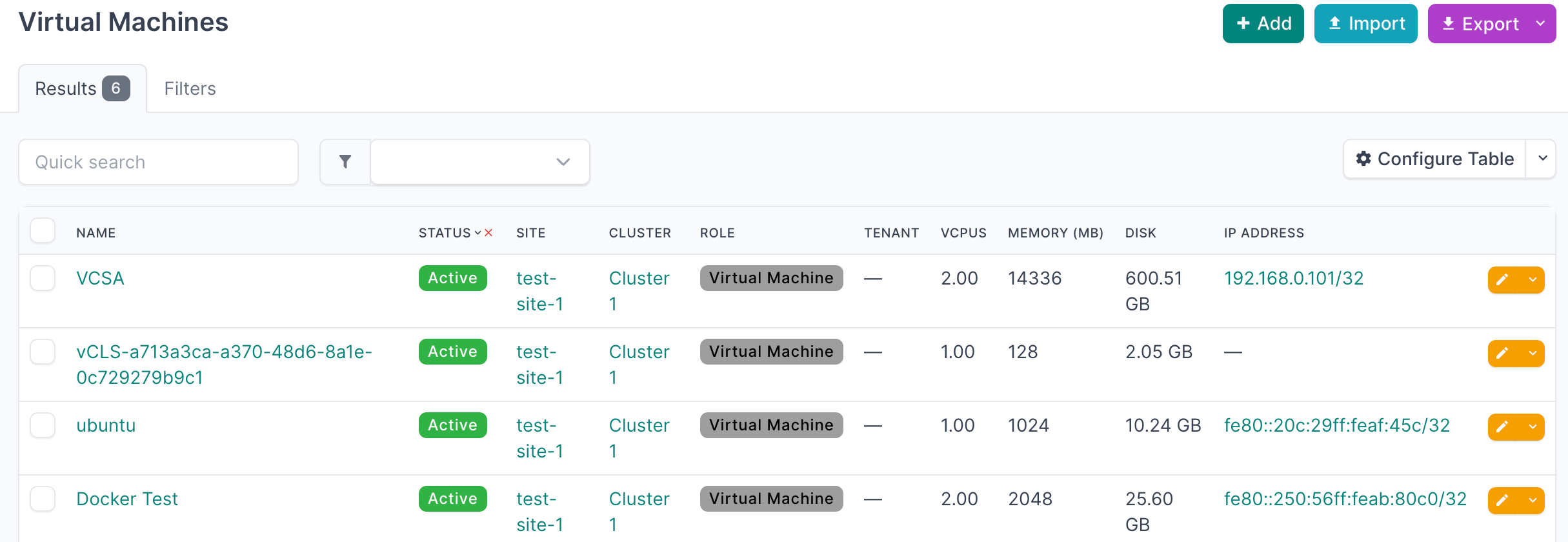
Now that you have run the integration at least once and applied the discovered data, you can view the data in the NetBox UI
- Start by clicking on Virtualization → Virtual Machines in the main navigation menu
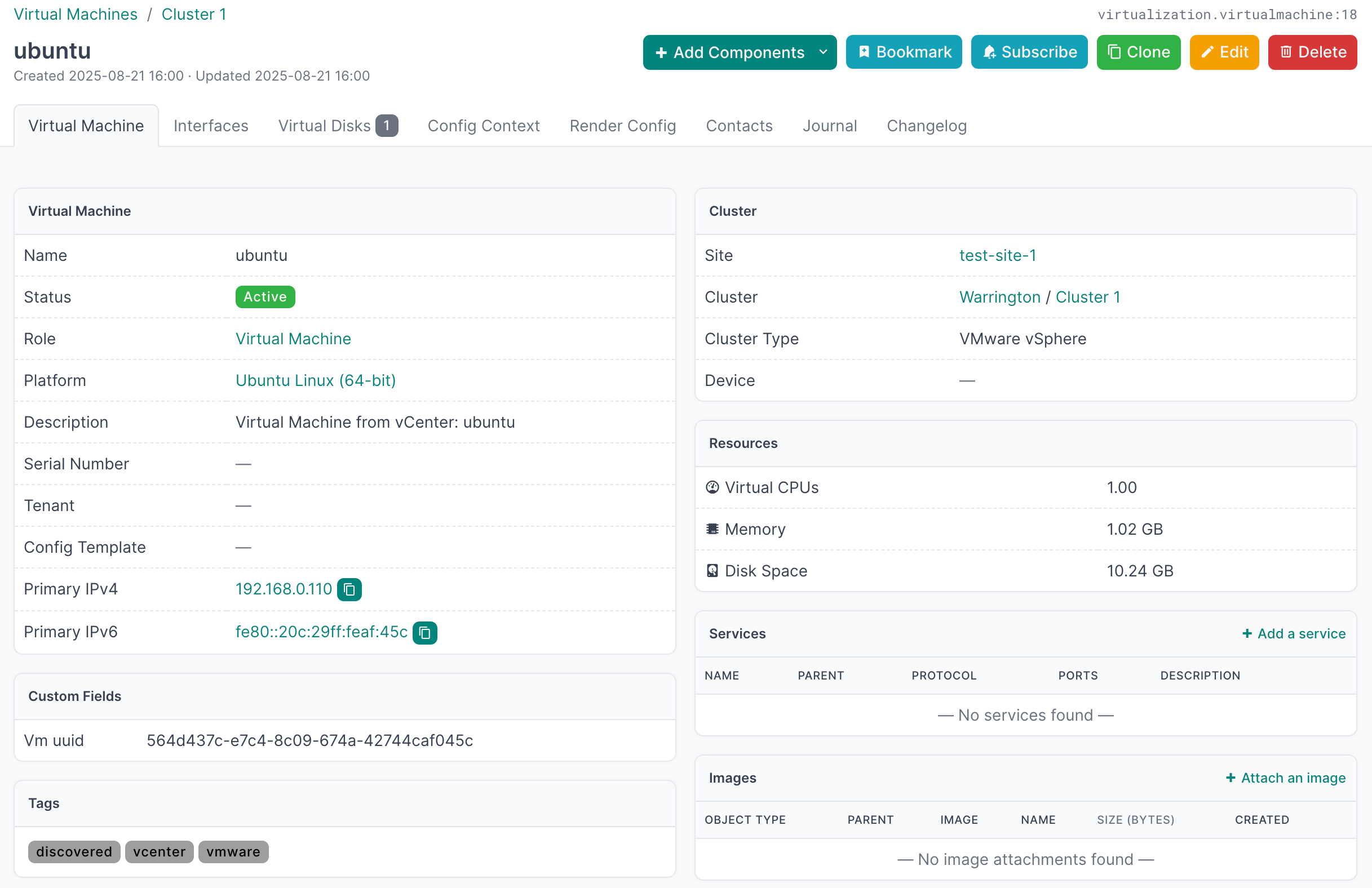
- Select an individual Virtual Machine to view the details
Additional Resources
Related Documentation
Support
Email support@netboxlabs.com for support.